Section: New Results
Fiber Based Video Segmentation
Participants : Ratnesh Kumar, Guillaume Charpiat, Monique Thonnat.
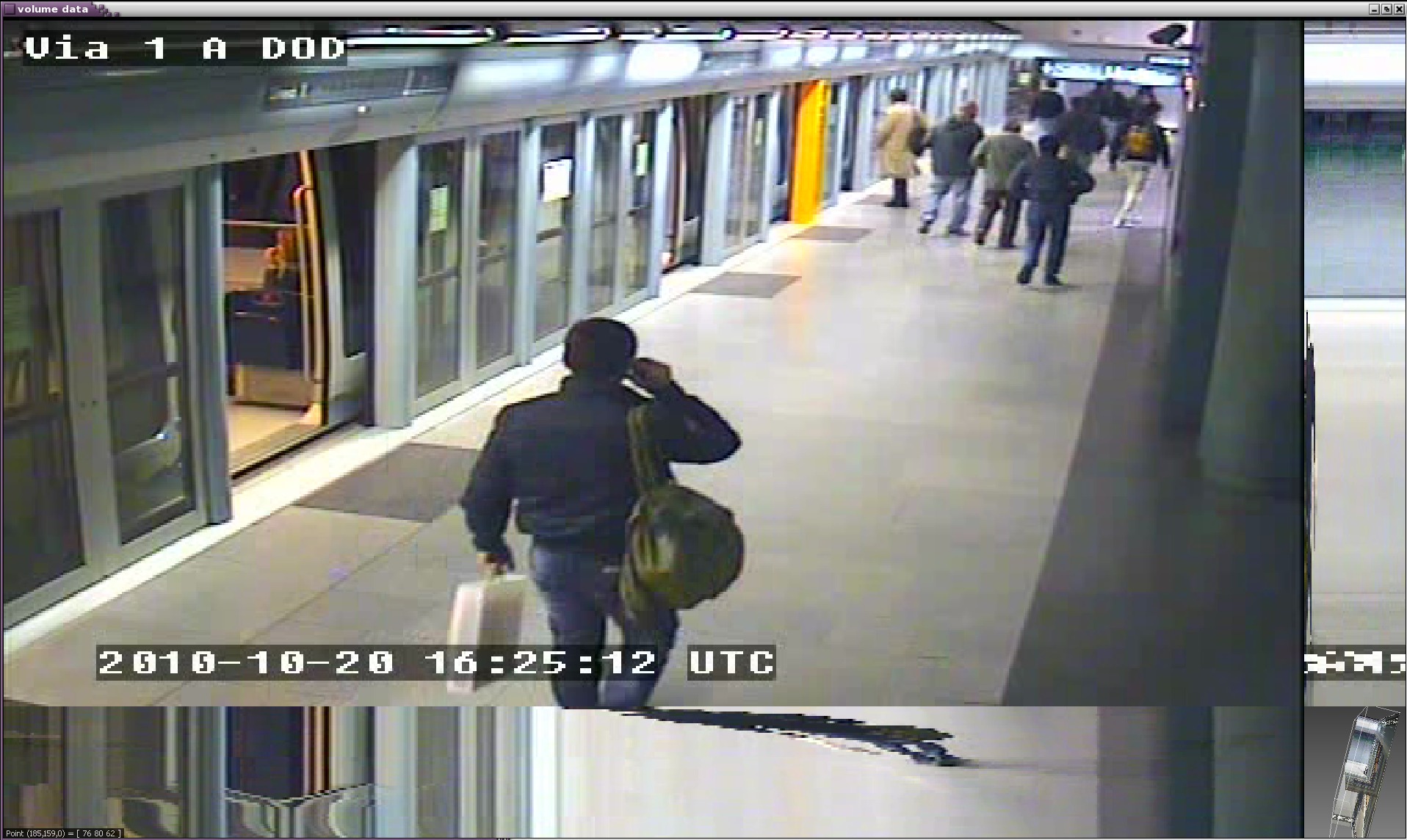
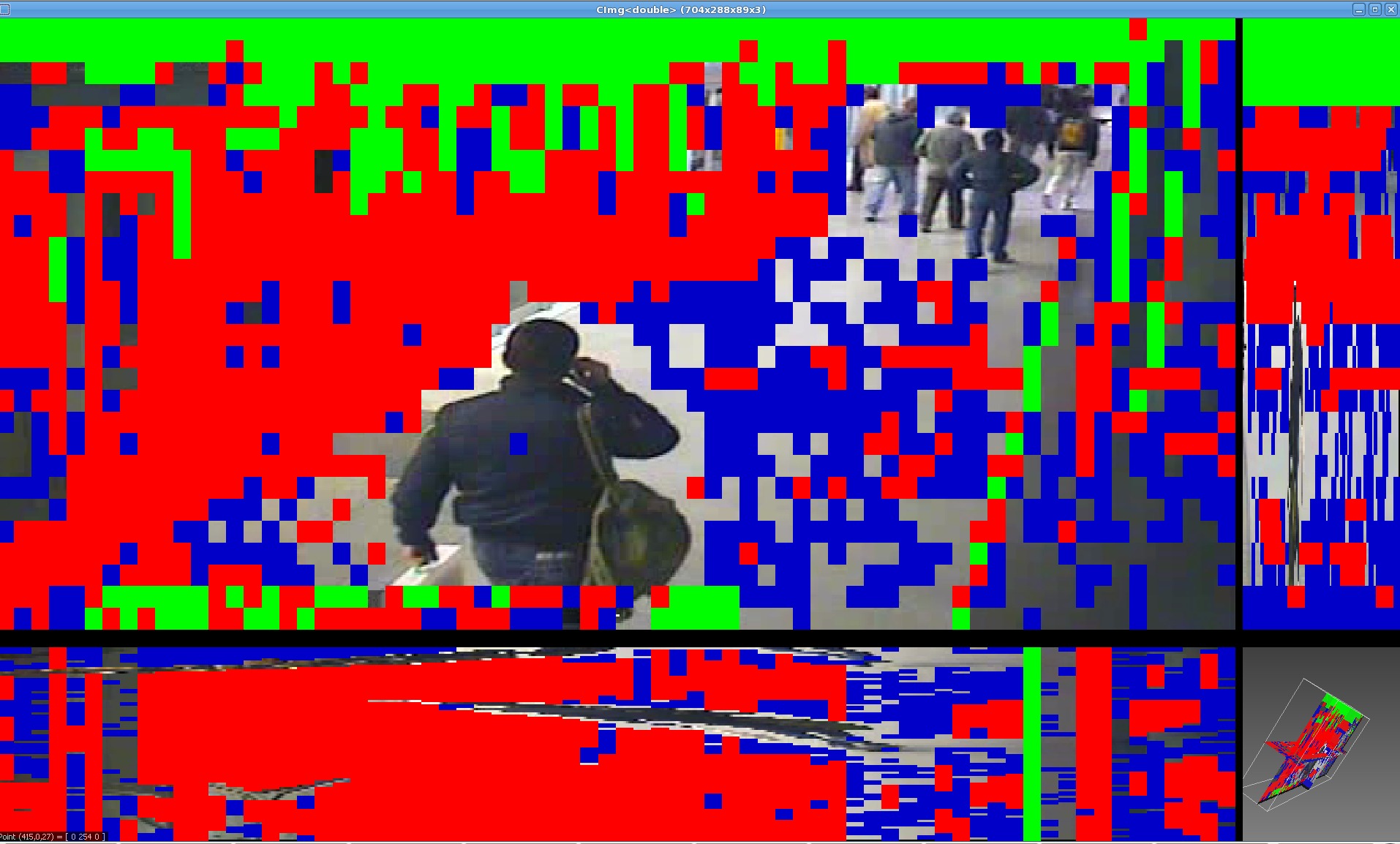
The aim of this work is to segment objects in videos by considering videos as 3D volumetric data (spacetime). Figure 11 shows 2D slices of a video volume. Bottom right corner of each figure shows the current temporal depth in the volume, while top right shows the X-time slice and bottom left shows Y-time slice. In this 3D representation of videos, points of static background form straight lines of homogeneous intensity over time, while points of moving objects form curved lines. Analogous to the fibers in MRI images of human brains, we name fibers, these straight and curved lines of homogeneous intensity. So, in our case, to segment the whole video volume data, we are interested in a dense estimation of fibers involving all pixels.
For the detection of these fibers, we use motion flow vectors and intensity correlation of 2D patches over time. As these techniques are not reliable everywhere in the image domain, we sort the fibers based on the reliability of the detections from these techniques. The subsequent goal is then to pick high ranked fibers to propagate motion information and boundary fronts to other regions of the 3D volume.
To reliably propagate information from a fiber, we express the reliability of detection of a fiber and the cost of propagation of information from it. The later can be based on a distance measure of a pixel from a fiber, while reliability of a fiber involves motion coherency, color homogeneity, duration along time axis etc.
Our work closely relates to [72] . A video is represented by a set of particles (trajectory of an image point sample). The algorithm then extends and truncates particle trajectories to model motion near occlusion boundaries.
Figure 12 shows some straight fibers found in a video volume. The reliability of these fibers is based on temporal length. Fibers which have temporal span same as that of the video are colored in green, while fibers which have temporal span of less than 10% of the video are colored blue. Red colored fibers have temporal length in between green and blue colored fibers.